Vitamins are substances that play an essential role in human metabolic processes, but which human cannot synthesize (except vitamin D). Small amounts of vitamins are essential for the regulation of all bodily processes. Vitamins must be obtained from the food on a daily basis. A person's diet must provide all the necessary vitamins. In their absence people develops certain deficiency diseases or other abnormal conditions.
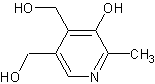
|
| Figure. Vitamin B6 Struture |
Vitamin B6 was essential for approximately 100 enzymes which catalyze essential chemical reactions in the human body. It's very important for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter, such as serotonin in the brain. Vitamin B6 functions as a coenzyme in the synthesis of heme, an iron-containing component of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells and is critical to their ability to transport oxygen throughout the body. Vitamin B6 was also important to the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Deficiency of Vitamin B6 was harmful to the human immune system. Severe Vitamin B6 deficiency can cause series neurologic symptoms like irritablity, depression and confusion. additional symptoms include inflammation of the tongue, sores or ulcers of the mouth, and ulcers of the skin at the corners of the mouth.
Foods containing large amount of Vitamin B6 including beans, nuts, legumes, eggs, meats, fish, whole grains, and fortified breads and cereals. The recommended Vitamin B6 intake from diet for an adult is 1.3 mg/day. Vitamin B6 is water-soluble.














