Vitamins are substances that play an essential role in human metabolic processes, but which human cannot synthesize (except vitamin D). Small amounts of vitamins are essential for the regulation of all bodily processes. Vitamins must be obtained from the food on a daily basis. A person's diet must provide all the necessary vitamins. In their absence people develops certain deficiency diseases or other abnormal conditions.
|
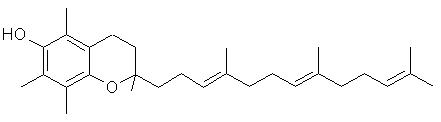
| Figure. Vitamin E Struture (alpha-Tocotrienol) |
Vitamin E is a generic term used for a group of chemically-similar compounds sharing the tocopherol and tocotrienol structures, . Vitamin E is an important anti-oxidant which protects against lipid peroxidation (which could contribute to cell membrane weakness).
Severe vitamin E deficiency results mainly in neurological symptoms, including impaired balance and coordination (ataxia), injury to the sensory nerves (peripheral neuropathy), muscle weakness (myopathy), and damage to the retina of the eye (pigmented retinopathy). The developing nervous system appears to be especially vulnerable to vitamin E deficiency. For instance, children who have with severe vitamin E deficiency from birth and are not treated with vitamin E rapidly develop neurological symptoms.
Foods contain large amount of Vitamin E include vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, wheat germ, green leafy vegetables. Vitamin E is fat-soluble.
















